What is the competitive edge that your business enjoys? Understanding your value proposition helps you to identify what makes your company special and what sets you apart from the competition. That’s important. But how can you tell if the things that make you special are creating value for your customers and a sizable profit margin for your company?
Value chain analysis is a way to analyze your business activities to determine how they provide a measurable benefit to your business and your customers. A value chain describes all of the business activities that it takes to create your product or deliver your service from start to finish. This includes design, production, distribution — everything that your business does to deliver to your customers.
This analysis allows you to identify your competitive advantage and areas for improvement. Ultimately, the goal of the analysis is to increase profit margins. Let’s take a more in-depth look at how value chain analysis can help your business:
What is Value Chain Analysis?
Value chain analysis provides a simple but effective way for businesses to evaluate the activities that they engage in to deliver their product or service. They can then use the results from the analysis to determine steps that they can take to improve their competitive advantage.
Competitive Advantage
A competitive advantage is what separates your business from your competitors in the minds of customers. To create a competitive advantage, you need to have a clear understanding of your ideal customers, target market, value that your product provides, and a solid understanding of the offerings of your competition. Put simply, a competitive advantage is the trait of your product or service that goes above and beyond the competitions in some way.
There are a few ways in which companies typically create a competitive advantage over the competition:
- Cost leadership. A good example of competitive advantage is cost leadership — or to become the lowest-cost provider in a particular market. Companies that are able to deliver higher volumes to customers can typically do so at a reduced cost. A great example of this would be McDonald’s, who use their standing within their market to secure better deals for themselves and pass those savings on to customers.
- Differentiation. Being different from the competition can be an advantage as well. By innovating within your market to deliver a product that is more useful or speaks to your audience in a different way, you set yourself apart. Differentiation allows you to charge a premium price for the product. A great example of this would be Apple, who charges a premium price for their electronics.
- Speed. Being able to deliver an equal-quality product in less time can be a huge competitive advantage in some industries. McDonald’s is also a good example of this, as they pioneered the fast food delivery model, setting them apart from the competition in their early days.
Value Chain Analysis Steps
There are several steps that are typically part of the value chain analysis process. The process as a whole requires a lot of research and can take time to develop. Before you begin to look at how your company will conduct your own analysis, it’s important that you understand what the different steps look like.
Value chain analysis really boils down to a three-step process. First, you look at your activities. Then you analyze the value associated with them, and finally, identify opportunities for improvement and optimization.
Step 1: Determine your primary and support activities.
The first step in the value chain analysis process is to determine what primary and support activities that make up your business processes. Work with your teams to outline the primary and support activities within your processes. These make up the value chain within your company. A value chain should include every action that is required in the development and delivery of your product.
Step 2: Analyze the value and associated costs of those activities.
Then, your team should brainstorm the different ways that each activity benefits your customers and your business. Compare the activities and steps in your value chain to the competitive advantage that you are trying to achieve. Do those activities help you to secure that competitive advantage?
Once the analysis of your processes is complete, you can then begin to calculate the cost of the activities. Identify which activities are labor intensive. Identify the activities that use costly materials. This will help you to determine which activities are cost-effective for your company and which are not.
Step 3: Identify opportunities for improvement to seize a competitive advantage.
Once the value chain analysis is complete, an overview of your findings should be delivered to executives and stakeholders in the analysis. This will help the company to find buy-in on where changes need to be made. A value chain analysis can help to give you an idea of how you can adjust your processes to deliver the most value to customers and to your business to increase profit margins and identify a competitive advantage.
Value Chain Analysis Diagrams and Templates
Value chain analysis is a process that is bolstered by the fact that businesses exist to create value for their customers. Organizations that have a deep understanding of how every activity they undertake works to the benefit of their customers will put themselves in a position for success.
Here’s an example of a value chain analysis chart:
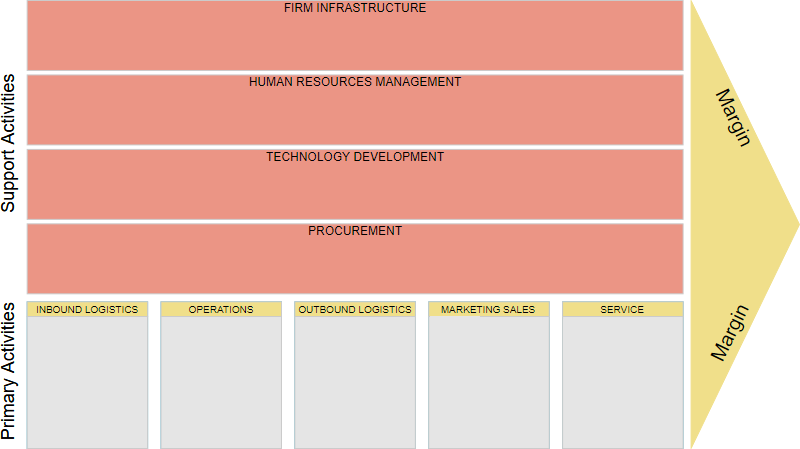
Source: Visual Paradigm
Here’s an example of what this template might look like for a supermarket store, factoring in all of the different operations and processes that they must consider in their shipping processes:
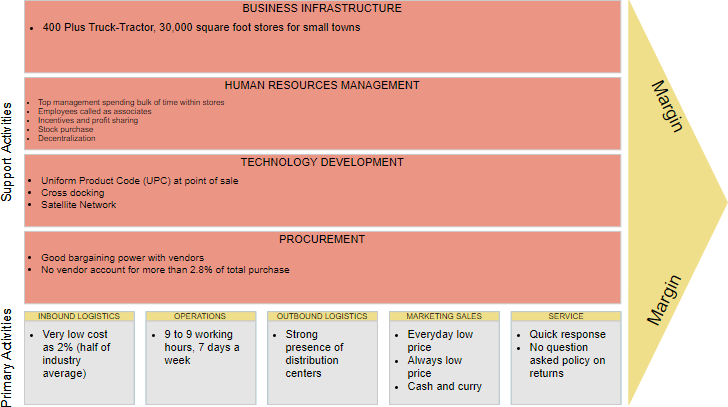
Source: Visual Paradigm
An Invaluable Addition
Value chain analysis gives your organization a bird’s eye view into your own operations and helps you connect every action that you take to specific benefits for your customers and your organization. It can be an insightful process for companies of any size. By deep-diving into your operations and individual tasks, you will be able to spot improvements and optimizations that can be made in your own processes to produce a better product for your customers and better outcomes for your stakeholders.

